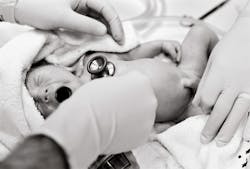
Global progress in reducing deaths of pregnant women, mothers and babies has flatlined for eight years due to decreasing investments in maternal and newborn health, according to a new report from the United Nations (UN). The report shows that over 4.5 million women and babies die every year during pregnancy, childbirth or the first weeks after birth - equivalent to 1 death happening every 7 seconds - mostly from preventable or treatable causes if proper care was available.
The report, Improving Maternal and Newborn Health and Survival and Reducing Stillbirth, assesses the latest data on these deaths - which have similar risk factors and causes - and tracks the provision of critical health services. Overall, the report shows that progress in improving survival has stagnated since 2015, with around 290 000 maternal deaths each year, 1.9 million stillbirths – babies who die after 28 weeks of pregnancy – and a staggering 2.3 million newborn deaths, which are deaths in the first month of life.
The COVID-19 pandemic, rising poverty, and worsening humanitarian crises have intensified pressures on stretched health systems. Since 2018, more than three-quarters of all conflict-affected and Sub-Saharan African countries report declining funding for maternal and newborn health. Just 1 in 10 countries (of more than 100 surveyed) report having sufficient funds to implement their current plans. Moreover, according to the latest WHO survey on the pandemic’s impacts on essential health services, around a quarter of countries still report ongoing disruptions to vital pregnancy and postnatal care and services for sick children.
Funding shortfalls and underinvestment in primary healthcare can devastate survival prospects. For instance, while prematurity is now the leading cause of all under-five deaths globally, less than a third of countries report having sufficient newborn care units to treat small and sick babies. Meanwhile, around two thirds of emergency childbirth facilities in sub-Saharan Africa are not considered fully functional – meaning they lack essential resources like medicines and supplies, water, electricity or staffing for 24-hour care.
In the worst-affected countries in Sub-Saharan Africa and Central and Southern Asia – the regions with the greatest burden of newborn and maternal deaths - fewer than 60% of women receive even four, of WHO’s recommended eight, antenatal checks.
To increase survival rates, women and babies must have quality, affordable healthcare before, during and after childbirth, the agencies say, as well as access to family planning services. More skilled and motivated health workers, especially midwives, are needed, alongside essential medicines and supplies, safe water, and reliable electricity. The report stresses that interventions should especially target the poorest women and those in vulnerable situations who are most likely to miss out on lifesaving care – including through critical subnational planning and investments.
Recent data show that only about 60% of women aged 15-49 years make their own decisions regarding sexual and reproductive health and rights.
Based on current trends, more than 60 countries are not set to meet the maternal, newborn and stillborn mortality reduction targets in the UN Sustainable Development Goals by 2030.