Reported cases of the sexually transmitted infections (STIs) chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis all increased between 2020 and 2021 – reaching a total of more than 2.5 million reported cases – according to CDC’s final surveillance data. To reverse this trend, CDC is calling for more groups from local, healthcare, industry, and public health sectors to contribute to STI prevention and innovation efforts.
The new report provides final surveillance data for 2021, and shows that overall in a single year (2020-2021):
- Gonorrhea rates increased more than 4%
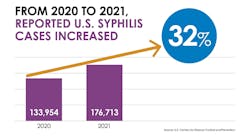
- Syphilis rates surged, increasing nearly 32% for combined stages of the infection
- Among the syphilis data, cases of congenital syphilis rose by an alarming 32% and resulted in 220 stillbirths and infant deaths.
- Chlamydia rates increased nearly 4%, but – unlike gonorrhea and syphilis – still did not return to pre-pandemic levels
- This raises concerns that screening continued to be impacted by COVID-19 related disruptions the second year of the pandemic, because the infection is often asymptomatic.
About the Author
Sign up for our eNewsletters
Get the latest news and updates